Picture this: you’re trying to learn a complex concept, and instead of reading boring text, you watch an engaging video, interact with animations, and take virtual field trips. This isn’t science fiction – it’s the reality of multimedia in e-learning today. As we advance into the digital age, the way we consume educational content is changing dramatically, and multimedia learning is leading this transformation.
The traditional classroom model of passive learning is quickly becoming outdated. Modern learners demand interactive, engaging, and visually rich content that speaks to their digital-native minds. This shift isn’t just a trend – it’s a fundamental change in how we approach education and professional development.
Table of Contents
What is Multimedia Learning?
Multimedia learning combines different types of content – text, images, audio, video, and interactive elements – to create a comprehensive educational experience. Unlike traditional learning methods that rely heavily on written materials, multimedia learning engages multiple senses simultaneously, making information more memorable and easier to understand.
Research shows that people retain 65% of visual information three days later, compared to only 10% of text-based information. This powerful statistic highlights why multimedia content has become essential in modern education. When learners can see, hear, and interact with content, they’re more likely to grasp complex concepts and retain information long-term.
The beauty of multimedia learning lies in its flexibility. Visual learners benefit from infographics and animations, auditory learners engage with podcasts and narrated videos, and kinesthetic learners interact with simulations and virtual environments. This multi-sensory approach ensures that diverse learning styles are accommodated within a single platform.
Why Multimedia in E-Learning Matters?
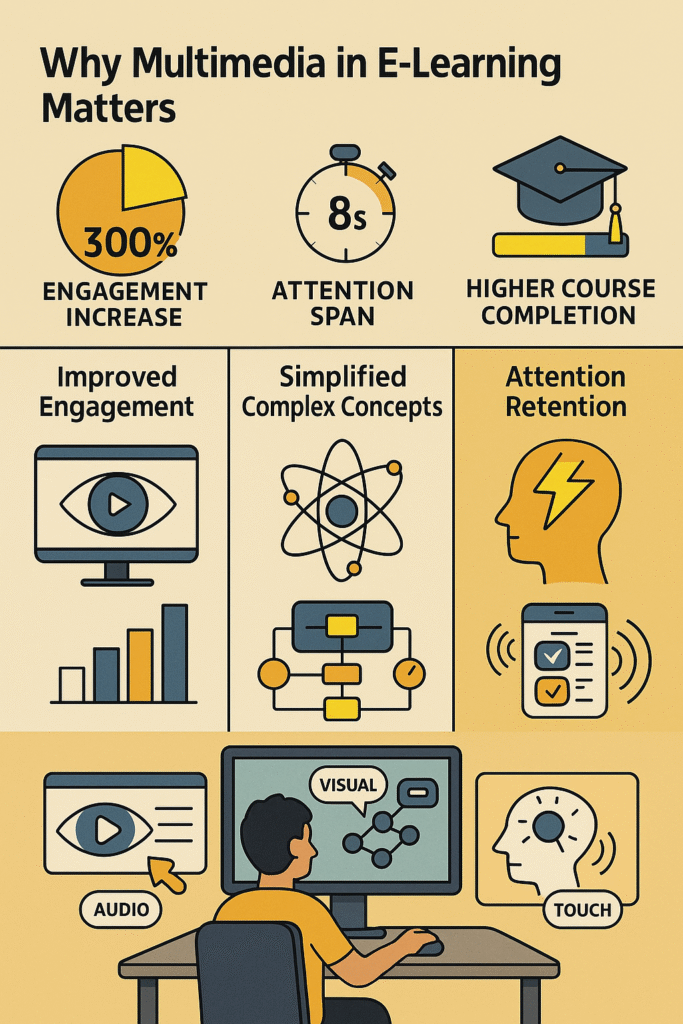
The importance of multimedia in e-learning extends far beyond making content more attractive. It addresses fundamental challenges in education and creates opportunities for enhanced learning outcomes.
First, multimedia content significantly improves engagement rates. Studies indicate that learners spend 300% more time on pages with multimedia elements compared to text-only content. This increased engagement translates directly into better learning outcomes and higher completion rates in online courses. This principle applies equally to educational institutions and corporate training environments, where employee engagement directly impacts productivity and skill development.
Second, multimedia learning breaks down complex concepts into digestible pieces. When you can visualise a process through animation, hear explanations through audio, and practice through interactive simulations, abstract ideas become concrete and understandable. This is particularly valuable in subjects like science, technology, and mathematics, where complex processes need clear visualisation.
Third, multimedia content caters to the shortened attention spans of modern learners. The average attention span has decreased to just 8 seconds, making it crucial to capture and maintain learner interest quickly. Multimedia elements provide the variety and stimulation needed to keep learners focused and motivated throughout their educational journey.
Implementing Multimedia in E-Learning
Text
While multimedia encompasses various formats, text remains the foundation of educational content. However, the way we present text has evolved significantly. Modern e-learning platforms use micro-learning techniques, breaking information into bite-sized chunks that are easier to digest. Interactive text elements, such as clickable definitions and expandable sections, make reading more engaging and purposeful.
Images
Visual elements serve as powerful learning aids that can explain concepts more effectively than words alone. High-quality images, diagrams, and illustrations help learners visualise abstract concepts and remember information better. Strategic use of images can reduce cognitive load and make complex information more accessible to diverse audiences.
Audio
Audio content, including podcasts, narrated presentations, and background music, adds another dimension to learning. It’s particularly valuable for auditory learners and provides flexibility for learners who prefer to consume content while multitasking. Quality audio production enhances the overall learning experience and can convey emotion and emphasis that text cannot.
Video
Video content has become the cornerstone of modern e-learning. It combines visual and auditory elements to create immersive learning experiences. From lecture recordings to animated explanations, video content can demonstrate processes, tell stories, and engage learners in ways that static content cannot match.
Animations
Animated content brings static concepts to life, making abstract ideas tangible and understandable. Animations are particularly effective for explaining step-by-step processes, scientific phenomena, and complex systems. They provide visual continuity that helps learners follow logical sequences and understand cause-and-effect relationships.
Creating Multimedia Learning Experiences
Storytelling
Effective multimedia learning often incorporates storytelling elements that create emotional connections with learners. Stories provide context, make content memorable, and help learners understand how concepts apply to real-world situations. When educational content follows a narrative structure, learners are more likely to stay engaged and retain information.
Educational storytelling can take many forms, from case studies that follow characters through challenges to historical narratives that bring past events to life. The key is creating relatable scenarios that help learners see themselves in the content and understand its relevance to their goals.
AR/VR for a Practical Approach
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) technologies are revolutionising practical learning by creating immersive environments where learners can practice skills safely. Medical students can perform virtual surgeries, engineering students can explore complex machinery, and history students can walk through ancient civilisations.
These technologies bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. The IEEE Computer Society reports that VR-based training can improve learning outcomes by up to 75% compared to traditional methods. As these technologies become more accessible, they’re increasingly integrated into mainstream e-learning platforms.
Infographics
Visual data representation through infographics makes complex information digestible and shareable. Well-designed infographics can convey statistics, processes, and relationships more effectively than lengthy text explanations. They’re particularly valuable for summarising key points and creating reference materials that learners can revisit.
Modern infographics often include interactive elements that allow learners to explore data at their own pace and focus on areas of particular interest. This interactivity transforms passive consumption into active engagement, enhancing the learning experience.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Multimedia Learning
Google Career Certificates
Google’s career certificate programs exemplify effective multimedia learning implementation. These courses combine video lectures, interactive exercises, hands-on projects, and peer discussions to create comprehensive learning experiences. The programs use real-world scenarios and practical applications to ensure learners can immediately apply their knowledge.
The success of Google’s approach is evident in its completion rates and job placement statistics. By incorporating diverse multimedia elements, they’ve created engaging programs that lead to tangible career outcomes for learners worldwide.
Microsoft Learning Paths
Microsoft has transformed technical education through their multimedia-rich learning paths. These programs integrate interactive labs, video demonstrations, documentation, and community forums to create immersive learning environments. Learners can practice skills in real cloud environments while receiving guidance through multimedia tutorials.
The effectiveness of Microsoft’s multimedia approach is demonstrated by its learner satisfaction scores and certification success rates. Their model shows how complex technical concepts can be made accessible through thoughtful multimedia integration.
Coursera’s Specialisation Programs
Leading universities partnering with Coursera have created specialisation programs that leverage multimedia learning extensively. These programs combine traditional academic rigour with modern multimedia presentation, including video lectures, interactive assignments, and peer-reviewed projects.
The global reach and success of these programs demonstrate how multimedia learning can democratize access to high-quality education. Learners from around the world can access world-class instruction through engaging multimedia content.
Multimedia Learning in Traditional Settings
Traditional educational institutions are increasingly incorporating multimedia elements into project-based learning. Students create videos, interactive presentations, and digital portfolios that demonstrate their understanding of concepts. These projects require students to engage with content creation tools and develop digital literacy skills alongside subject knowledge.
Mathematics education has been transformed through dynamic visual representations. Interactive geometry software allows students to manipulate shapes and observe how changes affect properties and relationships. These tools make abstract mathematical concepts tangible and help students develop an intuitive understanding of geometric principles.
Biology education benefits tremendously from multimedia integration. 3D anatomical models, interactive simulations, and virtual dissections provide students with detailed exploration opportunities that weren’t possible with traditional textbooks. These tools enhance understanding of complex biological systems and processes, allowing students to explore human anatomy in unprecedented detail.
Similarly, corporate training programs are leveraging multimedia learning to enhance employee skill development. Companies use interactive video modules for safety training, animated simulations for equipment operation, and virtual reality scenarios for customer service practice. These multimedia approaches reduce training time while improving retention rates and practical application of skills in real workplace situations.
Traditional classrooms are also incorporating Khan Academy resources, which use multimedia learning principles to explain complex concepts through engaging video content and interactive exercises.
The Emergence of Multimedia in E-Learning
Developing Technologies
The future of multimedia learning is being shaped by emerging technologies that promise even more immersive and personalised experiences. Artificial Intelligence is enabling adaptive learning systems that adjust content delivery based on individual learner progress and preferences.
Machine learning algorithms analyse learner behaviour to recommend optimal multimedia formats and pacing. This personalisation ensures that each learner receives content in the format most effective for their learning style and current knowledge level.
Interactive Experiences
Future multimedia learning will feature increased interactivity, allowing learners to manipulate content, explore scenarios, and receive immediate feedback. These interactive elements will blur the line between education and engagement, making learning feel more like discovery than instruction.
Accessibility and Inclusion
The future of multimedia learning prioritises accessibility, ensuring that content is available to learners with diverse abilities and circumstances. This includes closed captions, audio descriptions, and alternative text for images, making educational content truly inclusive.
The World Wide Web Consortium continues to develop accessibility standards that guide the creation of inclusive multimedia content, ensuring that technological advancement doesn’t leave anyone behind.
Mobile-First Design
As mobile devices become primary learning tools, multimedia content is being designed with mobile-first principles. This approach ensures that rich multimedia experiences are optimized for smaller screens and touch interactions, making learning accessible anywhere, anytime.
Conclusion: The Future of E-Learning
The integration of multimedia in e-learning represents a fundamental shift toward more effective, engaging, and accessible education. Success stories from Google, Microsoft, and Coursera prove that multimedia learning delivers real results for millions of learners worldwide.
The future of e-learning will feature even more immersive, personalised, and accessible multimedia experiences. Emerging technologies will create learning environments that adapt to individual needs and preferences, providing a more tailored learning experience.
For educators and organisations, the message is clear: multimedia in e-learning isn’t optional – it’s essential. Those who embrace these tools will create more effective learning experiences that prepare learners for success in our digital world.
Are you ready to join the multimedia learning revolution? The future of education is here, and it’s more exciting than ever before.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is multimedia learning, and how does it differ from traditional learning?
Multimedia learning combines text, images, audio, video, and interactive elements to create comprehensive educational experiences. Unlike traditional learning that relies heavily on written materials, multimedia learning engages multiple senses simultaneously, making information more memorable and easier to understand.
Why is multimedia content more effective than text-only learning?
Research shows that people retain 65% of visual information three days later, compared to only 10% of text-based information. Multimedia content caters to different learning styles and keeps learners engaged 300% longer than text-only content, leading to better learning outcomes.
What are the main types of multimedia elements used in e-learning?
The main multimedia elements include text (interactive and micro-learning format), images (diagrams and illustrations), audio (podcasts and narration), video (lectures and demonstrations), and animations (step-by-step processes and simulations).
How can educators implement multimedia learning in their courses?
Educators can start by incorporating storytelling elements, using AR/VR for practical applications, creating infographics for complex data, and integrating interactive videos and animations. The key is to match multimedia formats to learning objectives and student needs.
What role will AI play in the future of multimedia learning?
AI will enable adaptive learning systems that adjust content delivery based on individual learner progress and preferences. Machine learning algorithms will analyse learner behaviour to recommend optimal multimedia formats and pacing for personalised learning experiences.
Is multimedia learning accessible to students with disabilities?
Yes, when properly designed. Future multimedia learning prioritises accessibility through closed captions, audio descriptions, and alternative text for images. Following web accessibility standards ensures that multimedia content is inclusive for learners with diverse abilities.

0 Comments